2026 Facts About Flexography Printing You Should Know
January 01, 2026
Are you looking for a high-quality and cost-effective way to bring your next packaging project to life? Then you have likely heard the term "flexography". But what exactly is it, and why is it so important?
Flexographic printing is a cutting-edge method trusted by the packaging industry to produce large volumes of vibrant, durable prints on various materials like paper and foil.
Flexographic printing will grow by 4% annually through 2026. (Sources: Smithers Pira)
Whether you are already familiar with it or hearing about it for the first time, understanding this printing technique is key to seeing how it can benefit your packaging needs.
This blog will explain flexography printing and why it is a perfect solution for your next packaging challenge. Let’s get started.
What is Flexography Printing and Why It Matters in 2026
Flexography printing referred to as “flexo” is an efficient and high-speed printing method that uses flexible photopolymer plates and faster-drying inks to print on a wide range of substrates including:
- Paper
- Plastic
- Cardboard
- Metals
- Labels
- Films
- Cellophane
This printing method is ideal for large-volume production runs and can produce high-quality image resolutions with vivid colors.
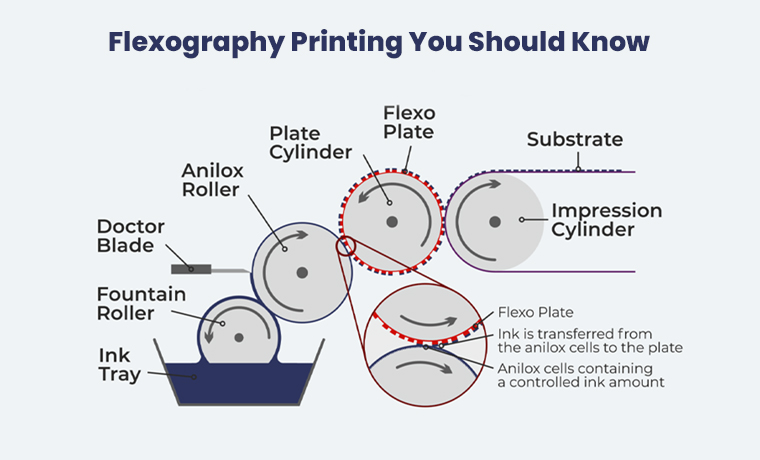
How The Flexography Printing Process Works?

The process of the flexography printing method begins when a photopolymer plate in a flexographic printing machine is attached to synchronously rotating impression cylinders.
Ink is transferred onto this flexible printing plate by an anilox roller intricately engraved with many smaller cells designed to retain and transfer the right amount of ink.
The printing substrate is fed into the process through an impression cylinder, a cylinder that exerts pressure to maintain constant contact between the flexographic plate and the substrate plate.
Choosing the Right Materials and Inks for Flexographic Printing
This flexographic technique is applied to a variety of materials. The inks can be different based on the printing media.
Paper and Cardboard
Paper and cardboard in this printing technique produce a wide range of paper packaging products, such as shipping labels or cardboard packaging.
Printing Plastic Substrates
Flexographic printing on plastic materials requires carefully selected low-viscosity inks for optimal absorption and adhesion. This method provides sharp and high-quality results.
Step-by-Step Flexographic Printing Process Breakdown
Flexographic printing includes three main phases: prepress, inking, printing, and post-press.
Pre-Press
This first process involves designing the artwork through design software and preparing the flexographic printing. As soon as the design is ready, the ink is transferred to the plates through a direct digital system. The plates are cut, mounted, and aligned on other plate cylinders.
Inking and Printing
The ink is transferred to the anilox rollers through a blade used on the rollers to remove excessive ink. Then, anilox rollers transfer the ink onto the flexo plates. After this, the plates transfer the ink to the substrates.
Post-Press
The final finishing and improved quality control techniques are applied to produce the product. The printed substrates are quickly dried. Then they are cut, folded, and laminated as per the requirements.
Note: Check the final product for defects. Make sure it is free from defects during packing, shipping, and storage.
Best Flexography Printing Examples in Top Markets and Industries
Here is the list of industries and markets using flexographic printing presses to meet their needs.
- Medical and pharmaceutical industry
- Food and Beverage industry for candy wrappers, cereal boxes, and packaging for various food products
- School and office supplies
- Boxes for product displays and point-of-purchase marketing materials
- Retail industry, from shopping bags and gift bags to other retail packaging materials
- Labels such as address labels and barcode labels
- Non-woven fabrics for diapers, wipes, and other non-woven products
Flexography Vs Offset Printing: Which is Better?
Here is the comparison between flexography and offset printing to highlight key differences.
| Features | Flexography Printing | Offset Printing |
| Printing Process | Uses flexible relief plates | Uses flat plates and rubber blankets |
| Ink Type | Fast drying with low viscosity inks | High-quality inks |
| Substrates | A wide range of substrates, such as paper, plastic, and metal | Primarily used for paper and cardboard |
| Image Quality | Good | High-quality and offers consistent reproduction |
| Print Speed | Faster and suitable for long runs | Slower but efficient for mid runs |
| Setup Time | Quick setup and turnaround | Longer setup and turnaround |
| Cost | Best for high-volume runs | Economical for mid-range volumes |
| Best For | Packaging, labels, newspapers | Books, magazines, brochures |
| Color Matching | It can be challenging as it requires adjustments | Excellent color consistency and accuracy |

Key Benefits and Drawbacks of Flexography Printing
Advantages of Flexographic Printing
Versatility
It can print a variety of substrates from plastic and brown papers to corrugated boards and acetate films, and can print high-quality patterns. It applies water-based inks, such as UV curable inks, utilizing a wide range of inks. These inks dry faster and are time-saving.
Highly Flexible Printing Method
This method can handle millions of impressions at a time and can accommodate a wide range of cylinder repeat lengths to meet customer needs.
Cost-Efficient
It is less expensive as compared to other printing techniques that require plates.
Consistent Ink Transfer
Its high-speed process and flexographic inks result in consistent and faster production with limited ink use.
Read More: What You Need To Know Printing on Sublimation Material
Disadvantages of Flexographic Printing
Printing
It is not capable of producing meticulous artwork like offset printing.
Expensive Equipment and Materials
The printing plates are costly as these plates are bought in different colors.
Unfit for Short Runs
Flexography printing is not suitable for small quantities.
Is Flexography the Right Fit for Your Business?
Flexographic printing is an economical and efficient technique when you need to print large volumes of packaging, labels, or flexible materials. However, it is not ideal for short runs.
Conclusion
You will have enough understanding about flexography printing through this guide. This efficient printing method utilizes flexible flexographic printing plates to produce high-quality images on various substances.
The best thing about this printing is its ability to print different types of materials, including packaging and labels, ensuring color and sharp details to enhance product appeal, which makes it ideal in various industries.
We have explored flexo printing's pros and cons with its applications and machines to help you understand its process from pre-press to post-press.
Talk to printing specialists ready to assist you from the platform of Custom Product Packaging in regards to choosing the modern printing technique for your next project. Don’t hesitate to email us at orders@customproductpackaging.com.





