In-Depth Guide to CMYK Printing: Explore More
November 19, 2025

Colors play a significant role in design, attracting eyeballs and influencing customers to make a final buying decision. That's right.
When it comes to printing your packaging design, don't you want to give it a striking appearance? Definitely, you want to make your packaging design stand out with enticing printing. The magic of CMYK printing can do wonders for you.
Thinking how? Stay with this blog to look inside the CMYK printing process and its pros and compare it with RGB to make an informed decision before choosing the right printing method.
What is the CMYK Color Model?
CMYK refers to Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (black). This subtractive color model is widely used in color printing to subtract light from a white background.
Unlike the RGB color model used in digital displays, CMYK produces desired shades on paper by combining four colors in various dot patterns and densities. This helps CMYK to reproduce a wide range of colors with the ink.
What Does CMYK Stand for?

CMYK stands for 4 colors as
- Cyan
- Magenta
- Yellow
- Key (black)
What Does Key Mean in CMYK?
The word "Key" defines the letter "K" in CMYK, which means black. It adds depth, sharp details, shading, and outlines to printed images. This helps in creating defined lines and details. Printers achieve a fuller range of colors and finer details by using black, aligning Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow.
What is the CMYK Printing Process?
The printing process of CMYK involves separating an image into four colors, Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black, and then layering these inks on the print material.
The inks mix and overlap to create various colors through layered dots. The beauty of the subtractive CMYK color model starts with the white paper by adding inks to produce a full-color image with depth and detail.
CMYK is ideal for printing brochures, magazines, and photos but not suitable for precise spot colors.
5 Steps of the CMYK Printing Process

- Design Creation
Using the CMYK color mode, graphics are created using software like Adobe Illustrator.
- Prepress Preparation
The design is separated into four colors (C, M, Y, K) to produce a printing plate for each color.
- Printing Plate Application
Each plate transfers its inks onto the printing substrates.
- Layering Ink
The inks are applied one by one and overlapped or mixed to produce the final image.
- Drying and finishing
The ink on print material dries when layered. This allows the inks to blend and set properly.
Role of Halftone Dots in Creating Colors in the CMYK Printing Process
Halftone is a group of tiny dots to create colors in CMYK. The size and shape of these dots determine the shades and intensity of the color. A human eye blends these dots into smooth and continuous colors through the Halftone process. These halftone dots found in two types are:
- Amplitude-modulated (AM)
- Frequency-modulated (FM)
The purpose of halftone dots is to achieve sharp and high-end printed materials by adjusting the size, shape, and placement of dots.
Key Benefits of CMYK Printing
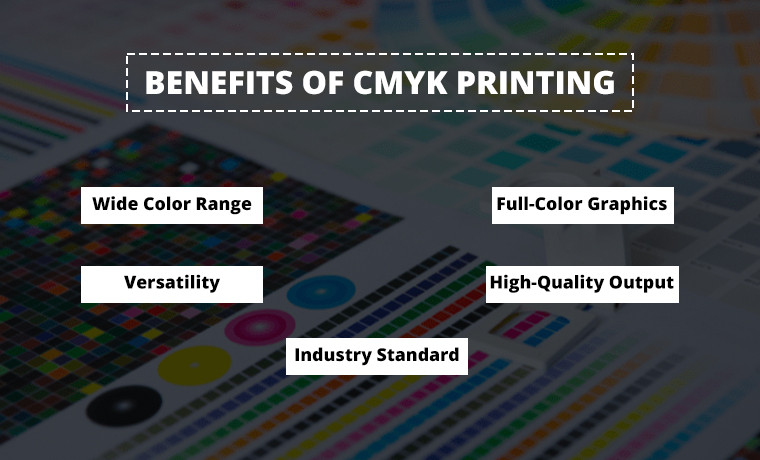
Here are the pros of using CMYK printing for more understanding.
- Wide Color Range
Producing millions of full, dark, vibrant, and rich colors makes CMYK ideal for printing full-color designs and graphics.
- Effective for Full-Color Graphics
Suitable for printing materials with various colors.
- Versatility
Compatible with various paper types and surfaces.
- High-Quality Output
Produces shape, vibrant, and professional-quality prints, including complex designs.
- Industry Standard
CMYK is globally used in the printing industry to ensure consistent results over different printers.
- Black Ink Improvement
Adding "Key" (black) improves contrast, detail, and text sharpness while minimizing the need for excessive color ink.
- Perfect for Mixed Content
Combining images and text makes CMYK an excellent choice for publications and marketing materials.
CMYK Vs RGB Printing: A Brief Comparison
Here is a brief comparison between CMYK and RGB to help you differentiate them in printing.
| Features | CMYK | RGB |
| Typical Colors | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (black) | Red, Green, and Blue |
| Color Model | Subtractive | Additive |
| Printing Uses | Printing on physical materials like paper and posters | Displays on digital screens like monitors |
| Color Creation | Creates colors by mixing ink on a surface | Colors are created by mixing light on a screen |
| Process | Ink is applied to paper, and subtracting light | Light is emitted by the screen and adds up to white |
| Best for | Books and brochures, etc. | Digital images, web design, and video displays |
Concluding Remarks
In the world of color reproduction, CMYK printing is ideal. It creates a wide spectrum of hues and shades and can take your packaging to new heights.
Whether you are designing a packaging box or labels, this CMYK color model is indispensable to creating accurate and vibrant results in printed materials.
Curious to know more about CMYK to elevate your printing game? The printing specialists at Custom Product Packaging can assist you better and show you how it can work best for your design. Ping us by sending us a quick email at orders@customproductpackaging.com.





